Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a critical waste treatment measurement in everything from municipal systems to food and beverage industry waste water streams.
COD - rapid determination method
It is now possible to get results for process control monitoring in a fraction of the time using any of the Hanna COD reagents.
The Rapid Method digestion time is reduced from 2 hours to 15 minutes when the digestion temperature is increased from 150°C to 170°C.
COD – Chemical Oxygen Demand is most often used indicator for analysis of effectiveness of purification of water treatment plant.
If the purification level is satisfactory, water can be discharged into receivers.
Analyzing the efficiency of purification means examining physical, chemical and biological indicators, water quality at the inlet and outlet of the purifier.
For the purpose of monitoring, standard analysis consists of physio-chemical indicators of wastewater quality:
- chemical oxygen demand (COD)
- biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
- concentration of suspended solids
- total phosphorus
- total nitrogen
Performing COD tests the right way is important in determining wastewater treatment effectiveness and can help diagnose any problems in treatment.
The COD method is also used in applications in power plants, chemical industry, paper industry, laundries, environmental studies and general education .
The efficiency of the treatment process is normally expressed as a percentage of oxidizable matter purified during the cycle.
In water purification plants, COD values must be less than 10 mg/l O2 at the end of the treatment cycle.
COD Determination
You can quantify the amount of trivalent chromium in a sample after digestion by measuring the absorbance of the sample at a wavelength of 600 nm in a photometer or spectrophotometer.
Alternatively, the absorbance of hexavalent chromium at 420 nm can be used to determine the amount of excess chromium at the end of digestion to determine COD values.
When a sample is digested, the COD material in that sample is oxidized by the dichromate ion.
As a result, chromium goes from hexavalent (VI) to trivalent (III). Both chromium species exhibit color and absorb light in the visible region of the spectrum.
In the 400 nm region the dichromate ion (Cr2O72-) absorbs much light while the chromic ion (Cr3 +) absorbs much less.
In the 600 nm region, it is the chromic ion that absorbs a lot and the dichromate ion has practically zero absorption.

This method is easy and requires just a few simple steps:
- Digest your samples and a reagent blank (The reagent blank is just a sample of deionized water that’s treated the same as your actual samples. You can even reuse the blank for as long as your reagent batch lasts)
- Let the digested samples and blank cool
- Zero the instrument using the blank vial
- Read the samples
HANNA pre-programmed methods cover the ranges:
- LR: 0-150 mg / l
- MR: 0-1500 mg / l
- HR: 0-15000 mg / l
- UHR: 0.0-60 g/L

What will you need for performing of a COD test?
COD Reactor + Photometer/Spectrophotometer + COD Reagents
1. Digestion heating block / COD Reactor
COD testing method requires the digestion step, so a heating block for your samples is crucial for ensuring accurate and repeatable results.
For best results, look for a heating block that features multiple temperatures so you have utility for other tests, such as total phosphorus. Most heating blocks also have timers, which are critical for keeping digestion times consistent over multiple runs.
For added safety, look for models that have an optional shield that covers the heating block in case of an accident.
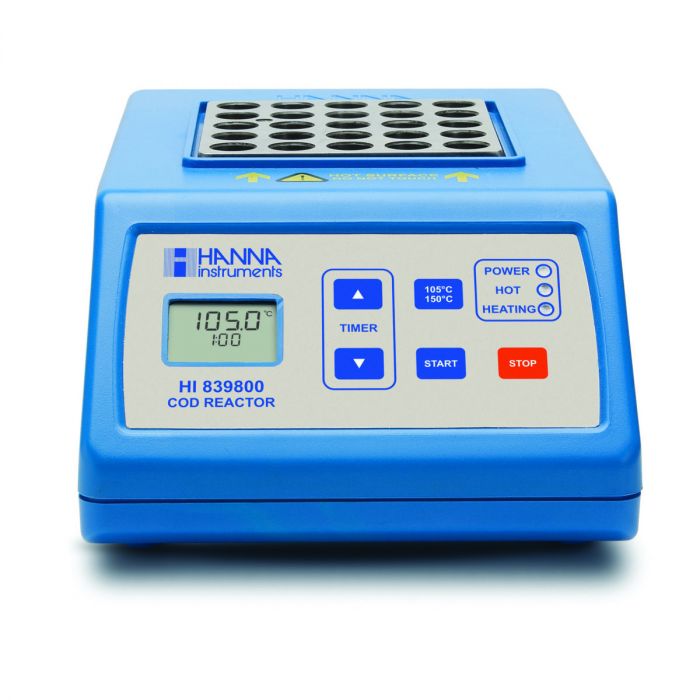
HI839800
COD Test Tube Heater
HI839800 COD Test Tube Heater with 25 Vial Capacity.
The HI839800 thermo-reactor is made of sturdy materials and has a vial capacity of up to 25 simultaneous digestions.
A built-in countdown timer of up to 180 minutes is included for applications that require timed digestions.
When this feature is enabled, a beep is heard and the heating element turns off at the end of the set time period.
Additionally, the reactor is set up with 3 predefined temperature programs that can be selected at the press of a button:
- 105 °C for total nitrogen digestion
- 150 °C for COD and total phosphorous reactions
- 170 °C for rapid method digestion
2. Photometer OR spectrophotometer
The photometer or spectrophotometer is the device that is going to read the absorbance of the samples after digestion in order to correlate it with the COD concentration.
Regardless of which instrument you choose, look for models that feature preprogrammed methods for COD for ease-of-use.
HANNA top picks are:
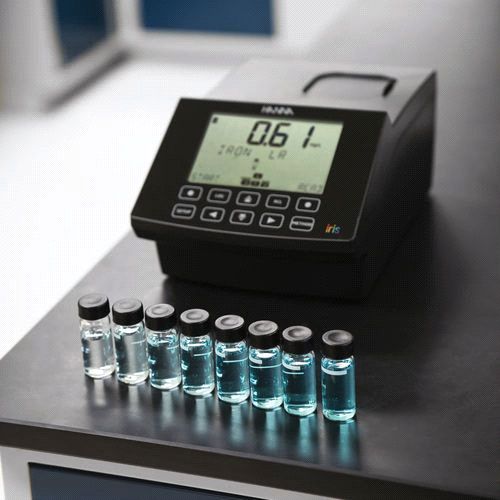
HI801
Iris Visible Spectrophotometer
The HI801 iris is a sleek and intuitive spectrophotometer that allows for measurement of all wavelengths of visible light.
Customize your methods, take a wide range of measurements, and feel confident in your testing accuracy with iris.
The convenience of pre-programmed methods with the option to expand.
Iris comes pre-programmed with more than 80 commonly used chemical analysis methods to help you get started. Simply update these methods by connecting to a computer or flash drive.
The goal in wastewater treatment is not only COD reduction, but also to control nitrogen and phosphorus, which are responsible for eutrophication phenomena in natural environments.
COD, nitrogen, and phosphorus control are performed not only to obey environmental protection laws, but also to optimize plant costs.
Effective monitoring and control of parameters such as ammonia, nitrate, total nitrogen and total reactive phosphorus allow plant managers to profile and improve the health of aquatic ecosystems.
By accurately monitoring levels of each specific pollutant, operational parameters can be adjusted to maintain high efficiency of biodegradation treatments while also minimizing costs.
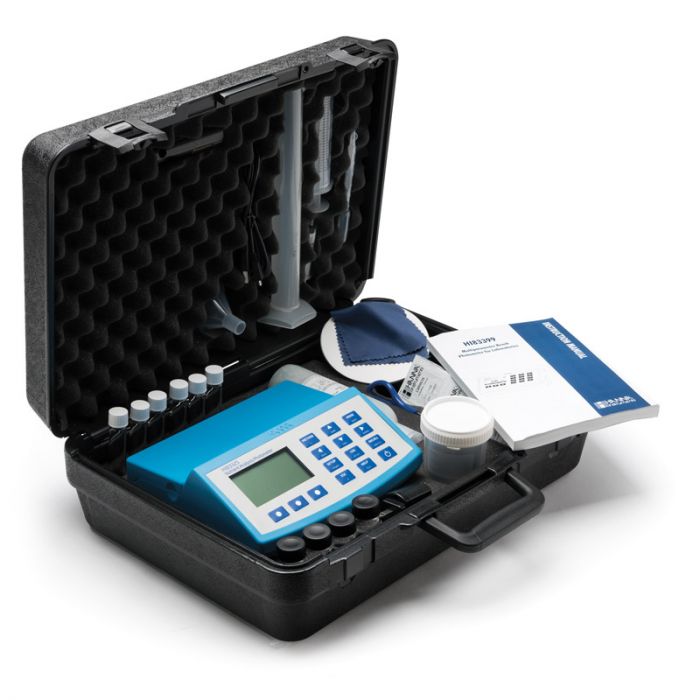
HI83399
Water & Wastewater Multiparameter (with COD) Photometer and pH meter
HI83399 is a compact, multiparameter photometer for measuring key water and wastewater quality parameters.
The meter is one of the most advanced photometers available with a innovative optical design that utilizes a reference detector and focusing lens to eliminate errors from changes in the light source and from imperfections in the glass cuvette.
40 key water and wastewater quality parameters with 73 different methods covering multiple ranges are programmed into the meter.
Wastewater treatment digestion parameters include COD, Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorous which are important for monitoring nutrient removal.
The HI83399 also offers an absorbance measurement mode for performance verification and for users that would like to develop their own concentration versus absorbance curves.
To save valuable laboratory benchtop space, the HI83399 doubles as a professional pH meter with its digital pH/temperature electrode input.
Now one meter can be used for both photometric and pH measurements.
HI97106
Chemical Oxygen Demand Portable Photometer

Low, Medium, High, Ultra High Range
The HI97106 is a waterproof, portable photometer with an advanced optical system designed to accurately determine chemical oxygen demand (COD).
With the CAL Check™ functionality, users are able to validate instrument performance at any time.
Hanna Instruments® CAL Check cuvettes are certified against NIST-traceable reference instrument(s).
The built-in tutorial mode guides users step-by-step through the measurement process.
The tutorial mode includes all steps required for sample preparation, the required reagents and quantities.
3. COD Pre-prepared reagents
Reagents are one of the most important components of the COD testing system. These chemicals are responsible for oxidizing the organic material.
Pre-dosed vials
Hanna vials contain approximately 3 mL of pre-dosed reagent. The operator just needs to add a small quantity of the sample.
Hanna COD reagents have been developed in accordance with Standard Methods 5220D, US EPA 410.4 and ISO 15705:2002 methods.
- ISO-compliant reagents: Conform to ISO 15705:2002 methods with respect to their composition. These compositions of these COD vials are similar to that of EPA standards, so they also contain mercury.
- Mercury-free reagents: Most COD vials contain mercury sulfate to remove chloride interferences, which would otherwise create a falsely high COD value. COD-free vials do not contain mercury, which makes them more susceptible to chloride interferences, but greatly reduce the safety and environmental risks of handling mercury. As a result, these reagents are ideal for routine analysis where no or very low chloride concentrations are expected.
4. Accessories
HI740217
Test Tube cooling rack
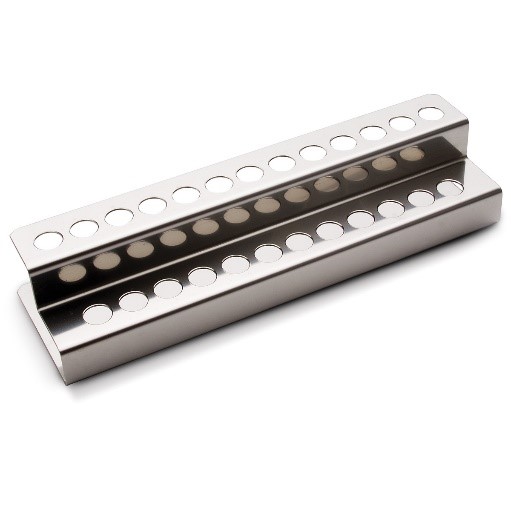

HI740216
Lab safety Shield

mag.ing.chem.ing
Have questions?
Contact a Hanna Technical Specialist at [email protected] or using our contact form.
SOURCES:
https://otpadnevode.hannainst.hr/
https://www.nrdc.org/stories/water-pollution-everything-you-need-know
https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/quality-and-wastewater/
http://silverstripe.fkit.hr/kui/assets/Uploads/6-509-514.pdf
https://interestingengineering.com/how-modern-wastewater-treatment-changed-our-world