Water disinfection is a critical step in ensuring the safety and cleanliness of drinking water.
Among the various disinfection methods employed, the use of free chlorine has been widely adopted due to its effectiveness against a wide range of harmful microorganisms.
Free chlorine refers to the combined amount of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite ion (OCl-) present in water, which act as powerful oxidizing agents. Accurate determination of free chlorine levels in drinking water is crucial to maintain optimal disinfection while avoiding potential health risks associated with excessive chlorine exposure.
This article provides an overview of the importance of free chlorine in drinking water, methods for its determination, factors affecting its concentration, regulatory guidelines, challenges in analysis, best practices for monitoring and future directions in the field.
1. Basics
We all know that water is essential for our survival. But what many of us might not think about is the quality of the water we drink. One important aspect of water quality is the presence of disinfectants, and one of the most commonly used disinfectants in drinking water is chlorine. In particular, free chlorine is a key parameter measured to ensure the safety of our drinking water.
2. Importance of Free Chlorine in Drinking Water
2.1 Disinfection Properties of Free Chlorine
When it comes to disinfecting drinking water, free chlorine is like the superhero of the water treatment world. Its main job is to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that can make us sick. By disrupting their cellular structures, free chlorine effectively kicks these pathogens out of our water supply. Talk about having the power to save lives, one glass of water at a time!
2.2 Health Benefits and Risks
While free chlorine plays a crucial role in ensuring clean and safe drinking water, like any superhero, it’s not without its flaws. Drinking water with the right amount of free chlorine can help prevent waterborne diseases and keep us healthy. However, excessive levels of free chlorine can lead to unpleasant tastes and odors in our water. So, it’s all about striking the right balance between effective disinfection and maintaining a pleasing drinking experience.
3. Methods for Free Chlorine Determination
There is several methods avaialable, most commonly used are
- Colorimetric methods
- Photometric methods
- Spectrophotometric methods
Determining free chlorine levels in drinking water is not as simple as just taking a sip and guessing. Thankfully, there are various methods available to accurately measure free chlorine. One common method is colorimetry, where a special chemical (DPD) is added to the water, resulting in a color change that can be correlated to the free chlorine concentration. It’s like magic, but with science!
DPD method
The Chlorine DPD (N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine) method is a widely used chemical test to measure the concentration of free and total chlorine in water samples. This method employs the reaction between chlorine and DPD, resulting in the formation of a colored compound. The intensity of color is directly proportional to the chlorine concentration, which enables accurate quantitative analysis. In this method, a reagent containing DPD and an oxidizing agent is first added to the water sample. The chlorine in the water reacts with DPD, producing a pink-colored solution. By comparing the pink color intensity to a calibrated color chart or analyzing it spectrophotometrically, one can determine both free and total chlorine levels accurately. Furthermore, this method offers high precision and sensitivity even at low concentrations, making it suitable for monitoring chlorine content in drinking water supplies, swimming pools, and industrial applications where maintaining proper disinfection levels is crucial for public health and safety.DPD Reagents
HI93701-01
Free Chlorine Reagents (100 tests)
HANNA offers high-quality reagents that are pre-measured, allowing users to achieve fast and accurate measurements with their HANNA family meters. These reagents follow the DPD Method in which the reaction between chlorine and reagent causes a pink tint in the sample.
By simply adding the packet of reagent to the sample, the reaction will take place and the instrument will determine the concentration from the color that is produced.
The results will be displayed in ppm (mg/L) of free chlorine.
Hanna Instruments to measure Free Chlorine
HI801
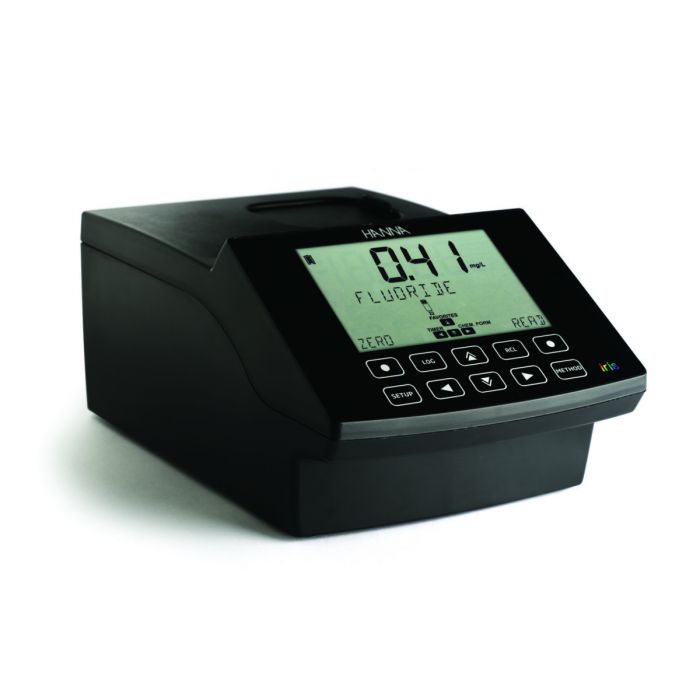
Spectrophotometer iris
IRIS portable spectrophotometer is unlike any of the products we have created in the past. It is different from our photometers as it allows for measurement in the spectrum of all wavelengths of visible light and not just pre-specified wavelengths. Spectrophotometers work by isolating light at specific wavelengths from white light.
This compact meter incorporates a number of features that facilitate both fantastic performance and exceptional usability.
- Advanced split beam optical system
- Rechargeable li-ion battery
- User customizable methods
Video tutorial:
Free Chlorine
determination method
HI97711
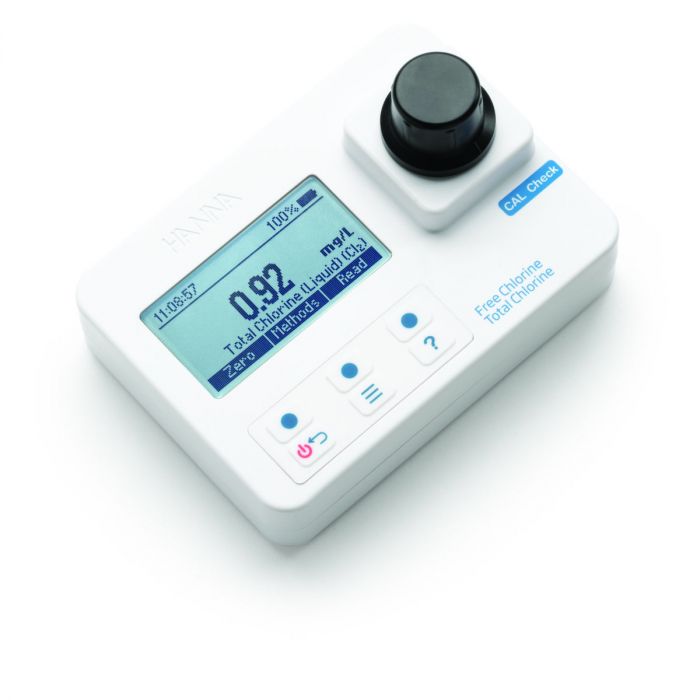
Free and Total Chlorine Portable Photometer
The HI97711 Free and Total Chlorine Photometer combines accuracy and ease of use in a simple, portable design.
The advanced optical system provides lab-quality accuracy while its user-friendly design is easy for any user making it the perfect photometer for your water quality testing needs.
The HI97711 meter measures free and total chlorine in water samples from 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L (ppm).
- No warm up time needed before taking a measurement
- Tutorial mode for easy step-by-step instructions
- Uses either powder or cost saving liquid reagents
- No warm up time needed before taking a measurement
- Tutorial mode for easy step-by-step instructions
- Uses either powder or cost saving liquid reagents
HI97711
Portable Photometer
Free and Total Chlorine
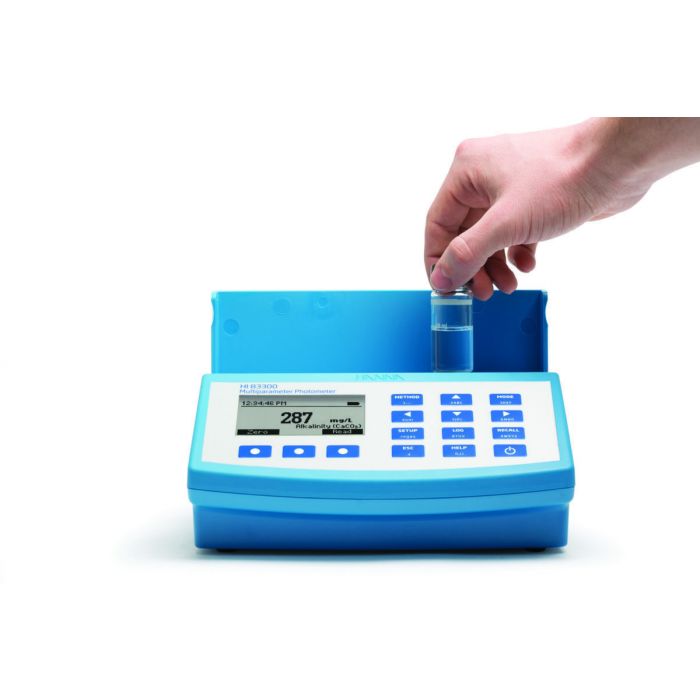
HI83300
Multiparameter Benchtop Photometer and pH meter
HI83300 is a compact, multiparameter photometer for use in the lab or in the field. The meter is one of the most advanced photometers available with a innovative optical design that utilizes a reference detector and focusing lens to eliminate errors from changes in the light source and from imperfections in the glass cuvette.
This meter has 60 different programmed methods measuring 37 key water quality parameters and also offers an absorbance measurement mode for performance verification and for users that would like to develop their own concentration versus absorbance curves.
To save valuable laboratory benchtop space, the HI83300 doubles as a professional pH meter with its digital pH/temperature electrode input. Now one meter can be used for both photometric and pH measurements.
- Advanced optical system
- Digital pH electrode input
⇒ Save valuable bench space with one meter that works both as a photometer and as a laboratory pH meter - Absorbance measuring mode
⇒ Allows performance verification using CAL Check standards
- Advanced optical system
- Digital pH electrode input
⇒ Save valuable bench space with one meter that works both as a photometer and as a laboratory pH meter - Absorbance measuring mode
⇒ Allows performance verification using CAL Check standards
HI701
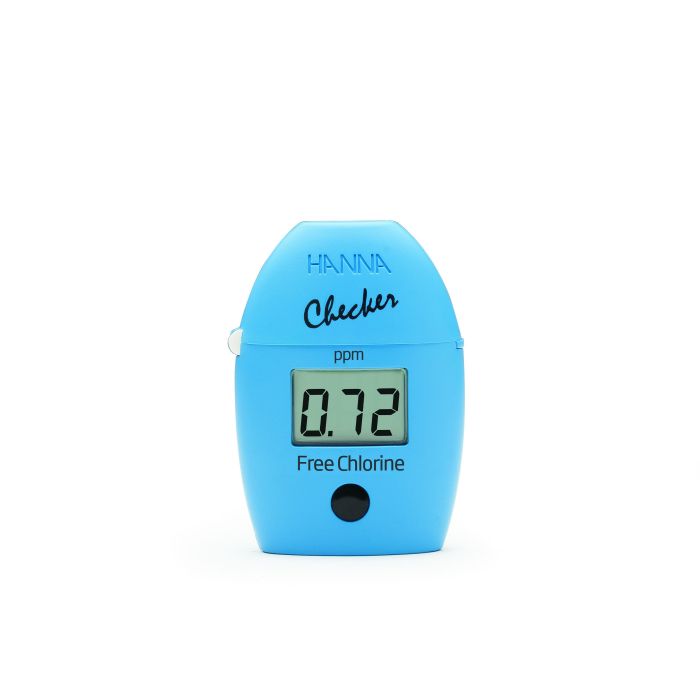
Hanna Free Chlorine Checker®
HANNA Checker bridges the gap between simple chemical test kits and professional instrumentation. Chemical test kits have limited accuracy and resolution since they rely upon the human eye to discern differences in color.
Professional instrumentation incorporates a light source such as an LED or tungsten lamp with a filter and a light sensing detector to precisely determine absorbance and ion concentration. Professional instrumentation offers greater resolution and accuracy but can cost hundreds of dollars.
The Hanna Free Chlorine Checker® uses a fixed wavelength LED and silicon photo detector to provide the accuracy of professional instrumentation at the affordable price of a chemical test kit.Compact, Portable Design
- Built-in Timer
- One-Button Operation
The Hanna Free Chlorine Checker® uses a fixed wavelength LED and silicon photo detector to provide the accuracy of professional instrumentation at the affordable price of a chemical test kit.Compact, Portable Design
- Built-in Timer
- One-Button Operation

HI701
Checker® HC
Free Chlorine
4. Factors Affecting Free Chlorine Concentration
4.1 Temperature
Who knew temperature could have such an impact on free chlorine? Well, it turns out that it does. Warmer temperatures can cause free chlorine to dissipate faster, potentially reducing its effectiveness as a disinfectant. So, if you want your chlorine to be the life of the party and keep those pathogens in check, make sure the water temperature is just right!
4.2 pH Levels
Sorry to bring up chemistry again, but pH levels also play a role in the free chlorine game. Lower pH levels can enhance the disinfection properties of free chlorine, while higher pH levels can hinder its effectiveness. It’s all about finding that pH sweet spot to ensure optimal disinfection. Don’t worry, you don’t need a pHd to figure it out!
How to measure the pH of drinking water fast and accurately?
4.3 Presence of Organic Matter
The presence of organic matter in water, such as leaves or algae, can bind with free chlorine, reducing its concentration and effectiveness. So, if your water has a lot of “natural” companions, it’s essential to monitor the free chlorine levels more closely. Keep those organic matter party crashers in check!
5. Regulatory Guidelines for Free Chlorine Levels in Drinking Water
When it comes to something as vital as drinking water, it’s no surprise that there are regulations in place to ensure its safety. National and international standards have been established to determine the acceptable levels of free chlorine in drinking water. These standards take into account factors such as the potential health risks associated with high chlorine levels and the efficacy of chlorine as a disinfectant.
6. Challenges and Limitations in Free Chlorine Determination
6.1 Interferences and Cross-Reactivity
Determining the concentration of free chlorine in drinking water is not without its challenges. Interferences from other substances present in the water can affect the accuracy of the measurements. Additionally, cross-reactivity between chlorine and other compounds can lead to false positives or false negatives. These factors need to be considered and addressed to ensure reliable and accurate free chlorine determination.
6.2 Sample Collection and Preservation
Another hurdle in free chlorine determination lies in the collection and preservation of water samples. Proper sampling techniques are necessary to obtain representative samples that reflect the true chlorine levels in the drinking water. Moreover, the samples must be properly preserved to prevent degradation of the chlorine compounds during transportation and storage. Failure to adhere to these protocols can compromise the accuracy of the analysis.
7. Best Practices for Free Chlorine Monitoring in Drinking Water
7.1 Proper Sampling Techniques
To ensure accurate and representative measurements, proper sampling techniques should be followed. This includes selecting appropriate sampling locations, using clean and properly sterilized equipment, and following standardized procedures for sample collection. Adequate training for operators involved in sample collection is crucial to minimize errors and ensure reliable data.
7.2 Calibration and Quality Control
Regular calibration and quality control are essential for maintaining accuracy in free chlorine monitoring. Calibration involves comparing the instrument readings to known standards to establish a relationship between the measured values and the actual chlorine concentrations. Implementing a robust quality control program ensures that the instruments are functioning correctly, and any deviations or errors are promptly identified and addressed.
HI97701-11
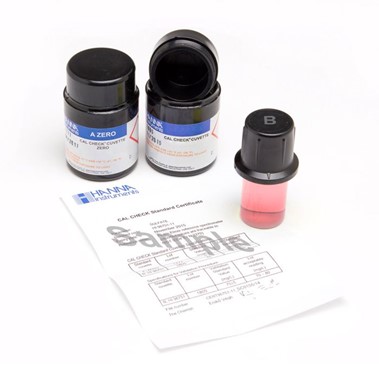
HANNA CAL Check
The HI97701-11 Free Chlorine Cal Check standards provides a simple solution to calibrating and validating the compatible free chlorine portable photometers that have a 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L (ppm) range. This high quality set of standards is manufactured in our state-of-the-art facility and comes supplied with a Certificate of Analysis.
The Certificate of Analysis provides the lot number, reference values and expiration date for traceability when certifying the appropriate free chlorine photometer.
- Pre-dosed reagents for ease of use
- Supplied with certificate of quality
- Marked with expiration date and lot number for traceability
7.3 Regular Maintenance of Monitoring Equipment
Monitoring equipment used for free chlorine determination should be regularly maintained to ensure optimal performance. This includes routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, calibration checks, and replacing worn-out parts. Regular maintenance improves the longevity of the equipment and reduces the chances of errors or malfunctions that can impact the accuracy of the measurements.
8. Conclusion

In summary, free chlorine determination in drinking water is governed by regulatory guidelines, both at the national and international levels.
Challenges such as interferences, sample collection and preservation, and analytical sensitivity, need to be overcome to ensure accurate results.
Have questions?
Contact a Hanna Technical Specialist at [email protected] or using our contact form.
AUTHOR:
Nives Vinceković Budor, mag.ing.chem.ing.

With Great Products
Come Great Results