First: Back to Basics 1
Permanent disinfection of your pool water is necessary and has two purposes:
Hygienic : destroy viruses, bacteria, parasites, etc. and eliminate the risks of contamination.
Safety : prevent the growth of algae and keep the water clean. Water without disinfectant, even if it is not used, quickly deteriorates due to the growth of algae and bacteria.
Why is hyperchlorination/shocking done in the first place?
For A-B-C reasons:
Algae: no matter which type of algae we are talking about, green/yellow/pink or black, the best algaecide is chlorine. Pool algae growth can be controlled with algaecide, but to kill algae and clear the pool, the best way is to shock it.
Bacteria & viruses: Bacteria can be found in a pool from various sources, they can be of the harmless variety, but we can’t disregard pathogenic bacteria which may also exist. (Shigella species; Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, Campylobacter and Salmonella, parasites (Cryptosporidium and Giardia), hepatitis A, noroviruses, coronavirus)
Chloramines: Combined chlorine molecules need to be broken apart! They are responsible for ‘red-eye’ and a strong chlorine smell. When Chloramine levels exceed 0.5 ppm (TC-FC=CC), add enough chlorine or non-chlorine shock to break apart the combined chlorine, usually 10-20x the tested CC level.
Back to Basics 2:
Chlorine
Chlorinated products are the substances most frequently used to maintain swimming pool water due to their high disinfecting power. The amount of chlorine is highly conditioned by the pH value, so it is recommended before chlorination to keep a clean pool, to achieve an optimal pH level.
We are usually talking about three different forms of chlorine:
Free Chlorine : This form has the greatest disinfecting and oxidizing power.
Combined chlorine : It has a very low disinfecting power and its presence causes irritations and bad odors.
Total chlorine : The sum of free and combined.
The guidelines for optimal values are:
Free: parametric value: 0.5 – 2.0 mg / l.
Combined: ≤0.6 mg / l.
How to calculate Combined Chlorine:
- Make measurement of Free Chlorine
- Make measurement of Total Chlorine
- Deduct the values:
Total Chlorine value – Free Chlorine value = Combined Chlorine Value
Combined Chlorine – Why this is so immportant?

While Free Chlorine is usually considered a Hero of the Day which does all the work all day long 24/7, Total Chlorine is in most cases totally left behind, similar to Ugly duckling story. Also, as the story goes, our story with Total Chlorine is quite similar. Without Total Chlorine you will not know how actually contaminated your pool is and what is the value of Combined Chlorine.
Chloramines result from the combination of two ingredients:
- chlorine disinfectants
- Bathers waste: perspiration, oils and urine that enter pools on the bodies of swimmers (main problem is ammonia).
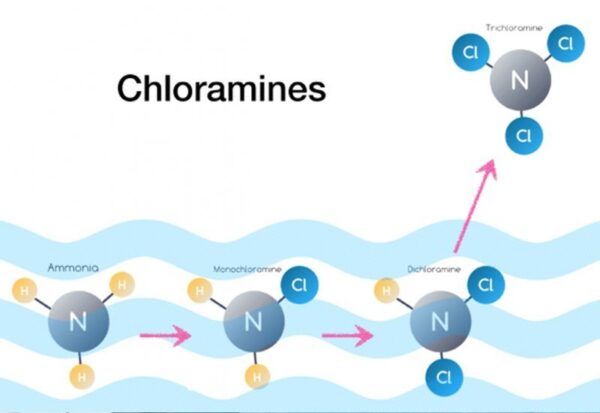
Chloramines (referred to as combined chlorine) are formed when water containing ammonia is chlorinated. There are three inorganic chloramine species: monochloramine (NH2Cl), dichloramine (NHCl2), and trichloramine (NCl3). The species of chloramines that are formed depends on factors such as the ratio of chlorine to ammonia–nitrogen, chlorine dose, temperature, pH, and alkalinity.
The principal reactions for chloramine formation are presented below:
HOCl + NH3 → NH2Cl + H2O
HOCl + NH2Cl → NHCl2 + H2O
HOCl + NHCl2 → NCl3 + H2O
What if you get the value of combined chlorine level 0.5 or higher?
It’s time for:
Hyperchlorination /shocking
Chlorine-based agents are most commonly used to disinfect pool water. Chlorine appears as an oxidant in various forms, as: sodium hypochlorite (liquid), calcium hypochlorite (tablets or granules) and the so-called organic chlorine (granules or tablets). Regardless of the chlorine in question, it is necessary to monitor the level of the so-called free chlorine, which in pool water must be in a concentration of up to 1.02 mg / l.
To properly dose the pool maintenance and chlorination agents, one must know how many cubic meters of water will fit in the pool. Depending on the shape of the pool, this can be calculated as follows:
Rectangular pool: length (m) x width (m) x depth (m) = pool volume (m3)
Round pool: diameter (m) diameter (m) x depth (m) x 0.78 = pool volume (m3)
Oval pool: length (m) x width (m) x depth (m) x 0.89 = pool volume (m3)
Eight-shaped pool: length (m) x width (m) x depth (m) x 0.85 = pool volume (m3)
The required dose for chlorination is 2g / m3 (2000 mg / m3) of water, and for hyperchlorination (chlorination shock) it is 20g / m3 (20000 mg / m3).
Hyperchlorination of pool water is carried out for the purpose of cleaning the pool. Hyperchlorinated water should be left in the pool for at least 24 hours to disinfect the pool walls. After that, the water should be drained from the pool, the pool should be filled with fresh water and continuous chlorination should be carried out. Hyperchlorinated water should not be used for bathing because it contains too much chlorine.

Hyperchlorination is also carried out in the case of microbiological contamination of pool water. Disinfection destroys microorganisms that are in the pool water and ensures bacteriologically correct bathing water. As pool water at a temperature of 25 ° C or higher is just an ideal habitat for the development of microorganisms, it is necessary to properly and regularly disinfect it and control the amount of free chlorine present in the water. Higher water and air temperature, and the presence of a larger number of bathers in the pool, proportionally increases the number of microorganisms in the water that multiply exponentially in such conditions. Precisely because of such a rapid multiplication of microorganisms, disinfection of pool water is crucial for the safety of bathers.
If the analyzed water samples from the pool SATISFY the conditions prescribed by the “Ordinance on sanitary-technical and hygienic conditions of swimming pools and on the health safety of pool waters” (OG 107/12) and the Ordinance on amendments to the Ordinance on sanitary-technical and hygienic conditions of swimming pools and on the health safety of pool waters “(OG 88/14) hyperchlorination is carried out once a year.
When water from a public water supply system (water supply system) is not used for filling the pool, but the pool is filled with water from another source (e.g. rainwater, water from a well), hyperchlorination is carried out more often depending on the use of the pool.
HANNA offers variety of testers and meters that can help you to better understand the balance of your pool and keep the water safe&clean:
HI971044 Pool Line Portable Photometer
Photometer is designed to measure pH, Alkalinity, Free & Total Chlorine, and Cyanuric Acid in swimming pools, hot tubs, and spas. This photometer combines accuracy and ease of use in a simple, portable design. The advanced optical system provides lab-quality accuracy while its user-friendly design is easy for any user, making it the perfect photometer for your water quality testing needs.
- No warm up time before taking a measurement
- Tutorial mode for step-by-step instructions
- CAL Check to verify meter performance

The HI97771 Free and Total (Ultra High Range) Chlorine Photometer combines accuracy and ease of use in a simple, portable design. The advanced optical system provides lab-quality accuracy while its user-friendly design is easy for any user making it the perfect photometer for your water quality testing needs. The HI97771 meter measures the free chlorine in water samples from 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L (ppm) and total chlorine from 0 to 500 mg/L (ppm).
HI7014 The Hanna Free Chlorine Checker® Handheld Colorimeter (HC)
bridges the gap between simple chemical test kits and professional instrumentation. Chemical test kits have limited accuracy and resolution since they rely upon the human eye to discern differences in color.
Professional instrumentation incorporates a light source at a specific wavelength and a light-sensing detector to precisely determine absorbance and ion concentration. The Pool Line Free Chlorine Checker® HC uses a fixed wavelength LED and silicon photo detector to provide the accuracy of professional instrumentation at the affordable price of a chemical test kit.
- Precise measurements with no guessing of color
- Laboratory measurements at a fraction of the cost
- Simple, intuitive operation

Author: Nives Vinceković Budor, mag.ing.chem.ing.
Sources:
https://www.stampar.hr/hr/hiperkloriranje-bazenske-vode
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/combined-chlorine






